Water-Based Concrete Stains vs. Reactive Acid Chemical Stains: Which is Right for Your Project?
When it comes to enhancing the appeal of your concrete surfaces, choosing the right stain can make all the difference. Water-based concrete stains and reactive acid chemical stains each offer unique benefits and challenges that cater to different preferences and project needs. Whether you're a homeowner looking to refresh your patio, a DIY enthusiast eager to tackle a new project, or a contractor seeking decorative concrete solutions, understanding these options is crucial. In this blog, we will provide a concrete staining comparison, highlighting stain durability, application methods, and color options to help you make an informed decision. Join us as we explore which type of stain will best suit your style and project requirements. #Understanding Concrete Stains
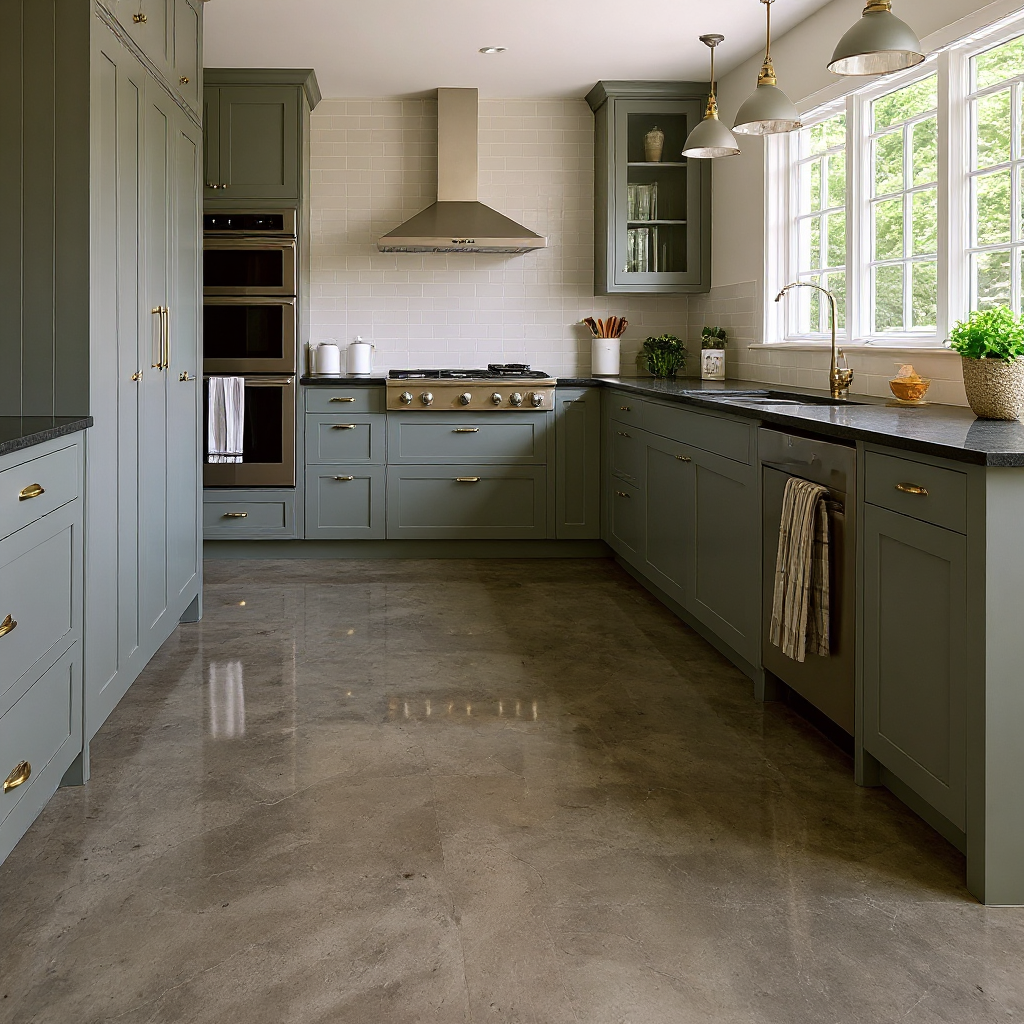

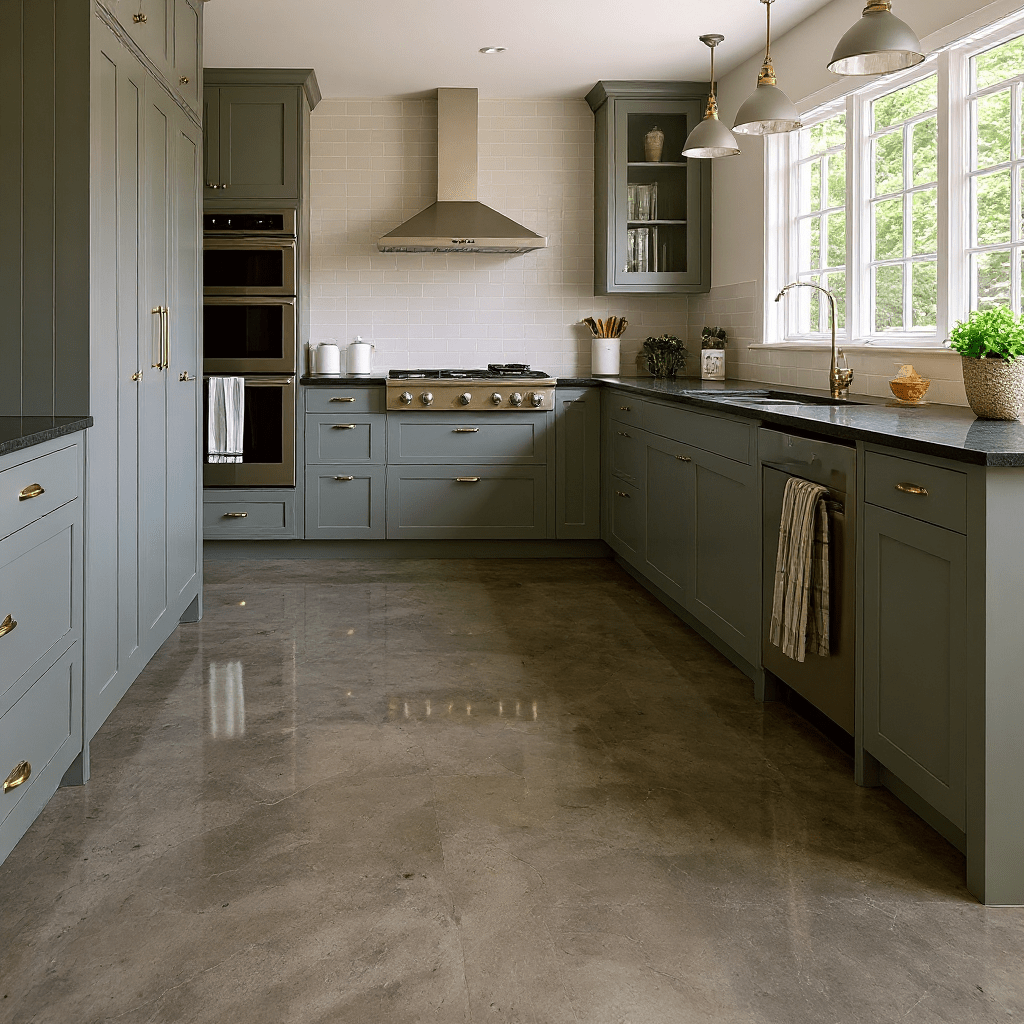
Concrete stain offers a way to transform plain surfaces into attractive, colorful spaces. Let's explore the two main types: water-based and reactive acid chemical stains.
Water-Based Concrete Stains Overview
Water-based concrete stains are a popular choice for many projects due to their ease of use and versatility. These stains work by depositing pigments onto the concrete surface, creating a layer of color.
Unlike their acid-based counterparts, water-based stains don't react chemically with the concrete. This means they offer more predictable results and a wider range of color options. Water-based stains are also known for their quick drying time and low odor, making them ideal for indoor applications.
One of the key advantages of water-based stains is their eco-friendly nature. They contain fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making them a safer choice for both the environment and the user. This factor has contributed to their growing popularity in recent years.
It is essential with a water-based stain however to make sure the concrete is porous (1/4 cup of water should soak into the concrete within 20-30 seconds), clean and well prepped to ensure the stain will achieve a good bond.
Reactive Acid Chemical Concrete Stain Basics
Reactive acid chemical stains work differently from water-based options. These stains contain metallic salts suspended in an acidic water-based solution. When applied to concrete, they react chemically with the calcium hydroxide in the surface.
This chemical reaction creates unique, variegated color effects that can't be replicated with other methods. The result is often described as having a natural, mottled appearance similar to marble or stone. Acid stains penetrate the concrete surface, creating a permanent color change.
It's important to note that the color palette for acid stains is more limited than water-based options. Typical colors include earthy tones like browns, tans, and blue-greens. The final color can also be influenced by the concrete's composition and age. Blue and green acid stains should never be used outside.
It is also important to note that no two slabs of concrete will color the same - if you have patches or sections of concrete that were poured at different times, it is more than likely they will stain a different shade.
Application and Durability

When choosing between water-based and acid stains, it's crucial to consider how they're applied and how long they'll last. Let's compare these aspects.
Comparing Application Methods
The application process for water-based and acid stains differs significantly, each with its own set of considerations.
Water-based stains are generally easier to apply. They can be sprayed, rolled, ragged or brushed onto the surface, much like paint. This makes them a popular choice for DIY projects. The application process typically involves:
-
Cleaning and preparing the concrete surface - make sure water readily absorbs into the concrete prior to staining.
-
Dilution: WRC stain comes in a concentrated form. You have to mix a minimum of 4 parts water to 1 part of stain. You can mix up to 8 parts of water to 1 part of stain for a more translucent shade. REMEMBER: You can always add more stain - it is much more difficult to take it away.
-
Applying the stain in thin coats - do not allow to puddle
-
Allowing each coat to dry before applying the next
-
Sealing the stained surface for protection - which sealer you use will be based on application area and foot traffic (Interior vs Exterior or Residential vs Commercial). It can also vary based on gloss level you desire.
Acid stains require more careful handling due to their chemical nature. The application process usually involves:
-
Thorough clean the concrete surface
-
Most common application is with an all-plastic pump-up sprayer, but other application methods are available.
-
Apply the stain heavy enough to saturate the concrete, but do not allow to puddle. Allow the stain to react for 4-5 hours. At this point you will see the residue come to the surface - this is not your color - it is just the residue - that will all need to be cleaned off to see your actual color.
-
Neutralizing the acid and rinsing the surface
-
Wash the surface until the water rinses off clear - at that point how it looks wet is about how it would look sealed (different sealers will enhance the color differently - the more solvents the deeper and richer the color will be)
-
Applying the appropriate sealer to protect the finish based on the application i.e. interior - exterior - commercial or residential
Stain Durability Insights
When it comes to durability, both water-based and acid stains can provide long-lasting results when properly applied and maintained. The sealer chosen is what ultimately protects the stain.
Water-based stains form a coating on the concrete surface. While this can make them more susceptible to wear in high-traffic areas, it also means they can be more easily touched up or reapplied if needed. With proper sealing and maintenance, water-based stains can last for many years.
Acid stains, on the other hand, penetrate the concrete and create a permanent color change. This makes them highly durable and resistant to fading. However, if the color does start to fade over time, it can be more challenging to refresh or change.
Both types of stains benefit from regular cleaning and periodic resealing to maintain their appearance and protect them from wear and tear.
Color and Aesthetic Choices

The final look of your stained concrete will depend largely on the type of stain you choose. Let's explore the color options and decorative possibilities.
Exploring Color Options
The color palette available for concrete stains varies significantly between water-based and acid options.
Concrete Resurrection water-based stains come in 34 different colors. This variety allows for more creative freedom in design. Some key points about water-based stain colors:
-
They can be mixed to create custom shades
-
Opaque and translucent options are available
-
Colors are generally more predictable
Acid stains, while more limited in color range, offer unique, variegated effects. Important considerations for acid stain colors include:
-
Typically, earthy tones like browns, tans, and terracotta
-
Some brands offer blue-green options (not to be used outside)
-
Final color will vary based on concrete composition
When choosing colors, it's important to consider the existing color of the concrete and how it might affect the final result. Always test the stain on a small, inconspicuous area before committing to the full project.
Decorative Concrete Solutions
Stained concrete offers a wide range of decorative possibilities, allowing you to create unique and attractive surfaces.
With water-based stains, you can achieve effects like color washing, antiquing, and even faux finishes that mimic wood or stone. These stains can be applied in layers or patterns to create depth and interest. Some popular techniques include:
-
Using stencils to create patterns or designs
-
Applying multiple colors for a marbled effect
-
Creating borders or accents in contrasting colors
Acid stains, while less versatile in color, create natural variations and mottling that can be highly attractive. They're often used to:
-
Create a natural stone look
-
Enhance the texture of stamped concrete
-
Achieve an aged or weathered appearance
Both types of stains can be combined with other decorative concrete techniques like scoring or engraving to create truly unique surfaces. The key is to choose a staining method that aligns with your design vision and the specific requirements of your project.